External CA
This information describes the supported and tested configurations for external CAs in this version of Puppet. If you have an external CA use case that isn’t listed here, contact Puppet so we can learn more about it.
Supported external CA configurations
This version of Puppet supports some external CA configurations, however not every possible configuration is supported.
-
Single CA which directly issues SSL certificates.
-
Puppet Server functioning as an intermediate CA.
-
If issues arise that are considered bugs, we'll fix them as soon as possible.
-
If issues arise in any other external CA setup that are considered feature requests, we’ll consider whether to expand our support.
Option 1: Puppet Server functioning as an intermediate CA
Puppet Server can operate as an intermediate CA to an external root CA.
See Using Puppet Server as an intermediate certificate authority.
Option 2: Single CA
When Puppet uses its internal CA, it defaults to a single CA configuration. A single externally issued CA can also be used in a similar manner.
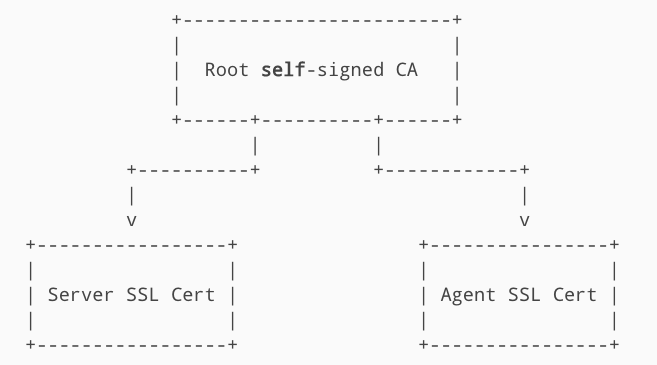
This is an all or nothing configuration rather than a mix-and-match. When using an external CA, the built-in Puppet CA service must be disabled and cannot be used to issue SSL certificates.
Puppet Server
-
Disable the internal CA service.
-
Ensure that the certname does not change.
-
Put certificates and keys in place on disk.
Puppet agent
You don’t need to change any settings. Put the external credentials into the correct filesystem locations. You can run the following commands to find the appropriate locations.
| Credential | File location |
|---|---|
| Agent SSL certificate | puppet config print hostcert --section
agent |
| Agent SSL certificate private key | puppet config print hostprivkey --section
agent |
| Root CA certificate | puppet config print localcacert --section
agent |
| Root certificate revocation list | puppet config print hostcrl --section
agent |
General notes and requirements
PEM encoding of credentials is mandatory
Puppet expects its SSL credentials to be
in .pem format.
Normal Puppet certificate requirements still apply
Any Puppet Server certificate must contain the DNS name, either as the Subject Common Name (CN) or as a Subject Alternative Name (SAN), that agent nodes use to attempt contact with the server.
Client DN authentication
Puppet Server is hosted by a Jetty web server; therefore. For client authentication purposes, Puppet Server can extract the distinguished name (DN) from a client certificate provided during SSL negotiation with the Jetty web server.
The use of an X-Client-DN request header is supported
for cases where SSL termination of client requests needs to be done on an external
server. See External SSL Termination with Puppet Server for
details.
Web server configuration
Use the webserver.conf file for
Puppet Server to configure Jetty. Several ssl- settings can be added to the webserver.conf file to
enable the web server to use the correct SSL configuration:
-
ssl-cert: The value ofpuppet server --configprint hostcert. Equivalent to the ‘SSLCertificateFile’ Apache config setting. -
ssl-key: The value ofpuppet server --configprint hostprivkey. Equivalent to the ‘SSLCertificateKeyFile’ Apache config setting. -
ssl-ca-cert: The value ofpuppet server --configprint localcacert. Equivalent to the ‘SSLCACertificateFile’ Apache config setting. -
ssl-cert-chain: Equivalent to the ‘SSLCertificateChainFile’ Apache config setting. Optional. -
ssl-crl-path: The path to the CRL file to use. Optional.
webserver.conf file might look something
like this: webserver: {
client-auth : want
ssl-host : 0.0.0.0
ssl-port : 8140
ssl-cert : /path/to/server.pem
ssl-key : /path/to/server.key
ssl-ca-cert : /path/to/ca_bundle.pem
ssl-cert-chain : /path/to/ca_bundle.pem
ssl-crl-path : /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/crl.pem
}Restart required
After the above changes are made to Puppet Server’s configuration files, you’ll have to restart the Puppet Server service for the new settings to take effect.